Introduction – Elon Musk’s Bold AI Ambition
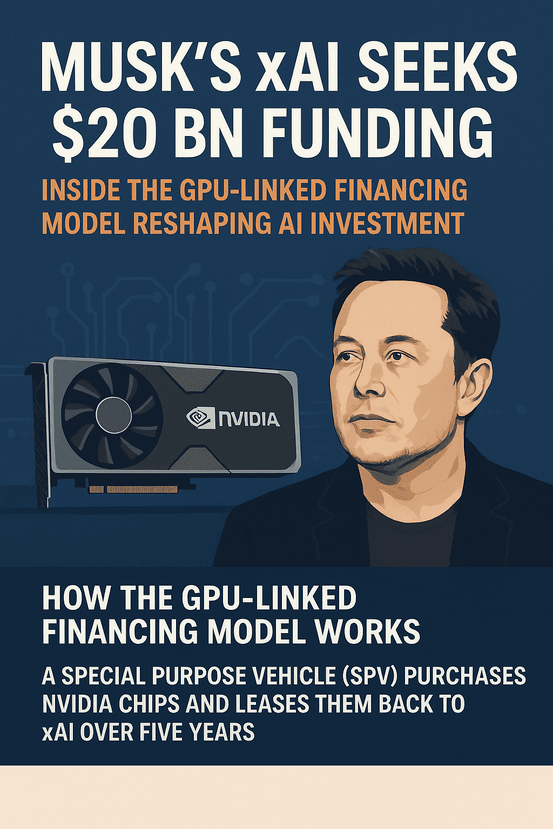
Elon Musk’s AI startup, xAI, is once again rewriting the rulebook—this time not through code, but through capital innovation. As Musk’s xAI seeks $20 billion funding, the company is introducing a financing model that could redefine how large-scale artificial intelligence ventures raise capital.

Founded to “understand the true nature of the universe,” xAI competes directly with OpenAI, Anthropic, and Google DeepMind. To keep pace, Musk’s company needs massive computational resources—primarily Nvidia GPUs, the backbone of AI training. But these chips don’t come cheap, with each H100 unit costing tens of thousands of dollars.
The solution? A GPU-backed financing model that turns hardware itself into a financial asset. It’s a bold, capital-efficient move in an industry known for astronomical costs.
The $20 Billion Fundraising Plan Explained
According to reports, xAI is raising around $20 billion through a mix of equity and debt financing. This will make it one of the largest private AI raises in history.
Equity and Debt Structure
The plan reportedly splits into roughly $7.5 billion in equity and up to $12.5 billion in debt. Nvidia is expected to take an equity position of up to $2 billion, strengthening its strategic partnership with Musk’s AI venture.
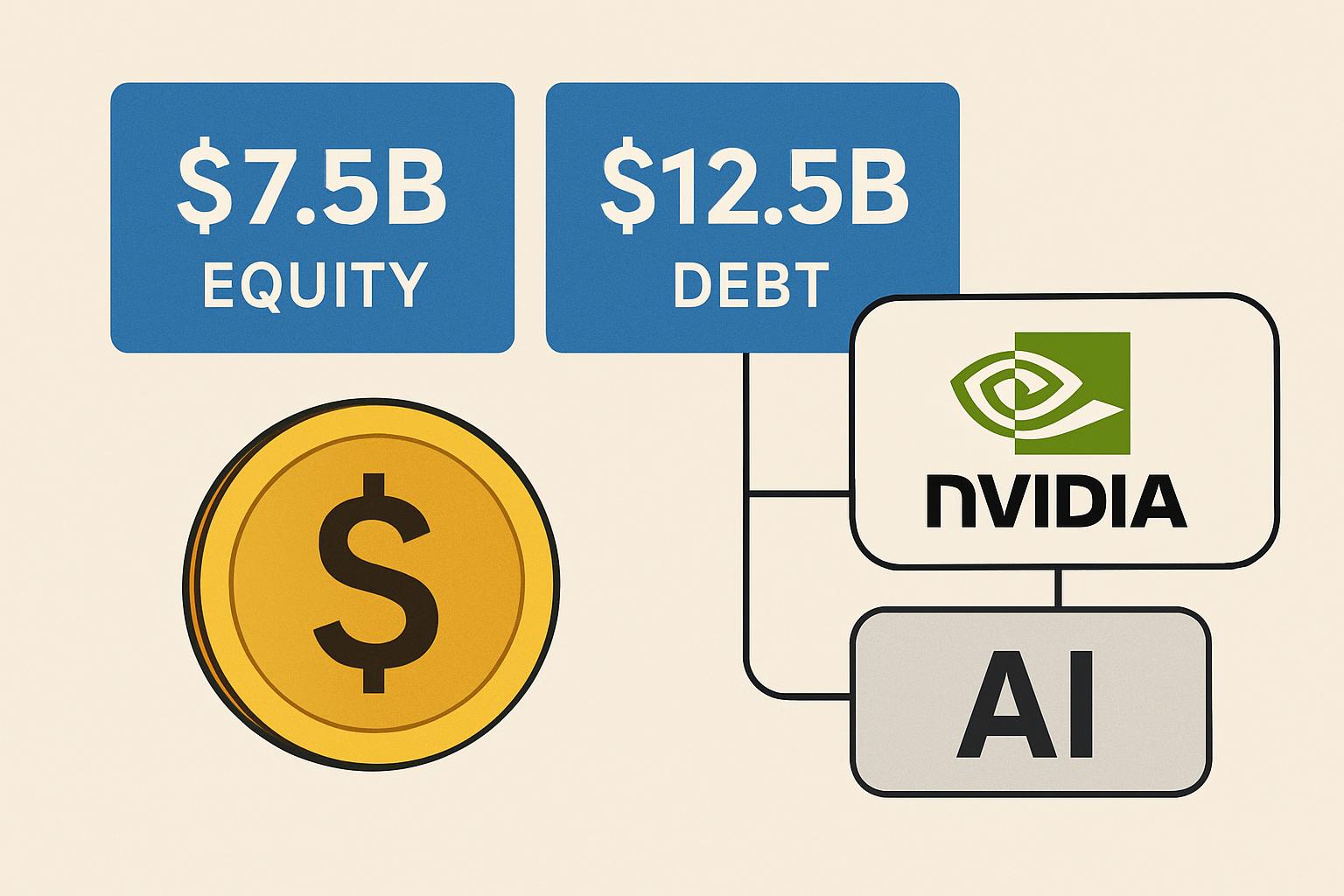
This hybrid structure allows xAI to expand aggressively without diluting too much ownership, while giving lenders tangible security via hardware-backed loans.
Role of Nvidia in the Funding Round
Nvidia isn’t just a supplier here—it’s a co-investor and enabler. Beyond providing GPUs, Nvidia supports the financing model itself, helping structure a deal that links hardware acquisition directly to capital access.
In doing so, Nvidia ensures continued demand for its chips while solidifying its role as both the technological and financial cornerstone of the AI ecosystem.
How the GPU-Linked Financing Model Works
The Special Purpose Vehicle (SPV) Mechanism
At the heart of this structure lies a special purpose vehicle (SPV)—a separate legal entity created solely to purchase Nvidia GPUs. Instead of xAI buying the chips outright, the SPV does so on its behalf.
This SPV then leases the GPUs back to xAI for a fixed term, typically five years. During that period, xAI makes scheduled payments, similar to leasing industrial equipment or aircraft.
Risk Management Through Hardware Collateral
Unlike traditional unsecured debt, this model gives lenders direct ownership over physical assets. Should xAI default, the lenders can reclaim or resell the GPUs to recover losses.
This setup significantly reduces lender exposure, making AI infrastructure investments more attractive to institutions wary of high credit risk.
Five-Year Leaseback Period and Payment Structure
The SPV structure usually involves a five-year amortization schedule. Payments are calibrated against hardware depreciation, meaning lenders recover most of their capital through asset value retention rather than company cash flow alone.
Key Players and Financial Backers
Three major financial institutions are backing the structure:
- Apollo Global Management – one of the largest private equity and credit firms, offering structured debt and asset-based financing.
- Diameter Capital Partners – a hedge fund specializing in opportunistic credit investments.
- Valor Capital – focusing on cross-border growth investments, bringing strategic connections between the U.S. and Latin America.
Together, these firms bridge Wall Street sophistication with Silicon Valley innovation.
Why GPU-Backed Financing is a Game-Changer for AI Startups
The biggest bottleneck for AI startups is capital intensity. Training large-scale models requires billions in GPUs, data centers, and energy. Traditional debt investors hesitate to fund such ventures because they lack tangible collateral.
The GPU-backed financing model changes that equation.
Reducing Lender Exposure and Credit Risk
By anchoring loans to the physical value of GPUs, lenders are shielded from direct business volatility. Even if xAI faces setbacks, the hardware retains residual value. This transforms AI financing from speculative venture lending into asset-secured credit.
Expanding Access to Capital for AI Infrastructure
Smaller AI firms could replicate this model, creating hardware leasing markets where chips are financed, owned, and recycled efficiently. It’s a model that bridges finance and technology—bringing Wall Street discipline to Silicon Valley’s innovation.
Potential Risks and Challenges of the Structure
While groundbreaking, the model isn’t without pitfalls.
GPU Depreciation and Secondary Market Risks
Nvidia’s chips evolve quickly. What’s top-tier today may be outdated in two years. If resale markets become saturated or if technological leaps occur, the collateral’s value could fall sharply, exposing lenders.
Legal and Operational Complexities of SPV Leasing
SPV structures add legal overhead. Issues like chip maintenance, insurance, and replacement obligations could create disputes between lenders, lessors, and xAI.
Implications for the Future of AI Financing
A Blueprint for Hardware-Secured Lending
If successful, xAI’s model may inspire a wave of asset-backed AI financing—where GPUs, data centers, or specialized chips become tradable financial instruments. This could dramatically expand access to institutional capital for deep-tech startups.
Nvidia’s Emerging Role as Financier and Partner
For Nvidia, this marks a new frontier. The company isn’t just a hardware supplier—it’s now a strategic financier in the AI ecosystem. That dual role strengthens its moat and creates new revenue streams beyond chip sales.
Industry Reactions and Expert Opinions
Market analysts view the deal as both innovative and risky. Some praise it as a masterstroke that de-risks AI financing, while others warn of potential asset bubbles if too many firms adopt GPU-backed loans without strong demand fundamentals.
Still, the consensus is clear: this move cements Musk’s position as an AI industry disruptor—not only in technology but also in how the sector finances itself.
FAQs About Musk’s $20 Billion xAI Funding Round
1. What is the total funding xAI is seeking?
xAI is raising approximately $20 billion, combining equity and debt financing.
2. How does the GPU-backed financing model work?
A separate SPV buys Nvidia GPUs and leases them to xAI. Lenders are repaid through lease payments, with GPUs serving as collateral.
3. Who are the key investors involved?
Nvidia, Apollo Global Management, Diameter Capital Partners, and Valor Capital are primary participants.
4. Why is this structure significant?
It reduces lender risk, making it easier for capital-intensive AI companies to secure financing.
5. What are the potential downsides?
Hardware depreciation, complex leasing terms, and uncertain secondary market values pose challenges.
6. Could this become a trend?
Yes—if successful, this structure could redefine how AI infrastructure projects are financed globally.
Conclusion – A New Era of Capital-Efficient AI Financing
Musk’s xAI seeks $20 billion funding not just to build more powerful AI models, but to pioneer a financial model that balances innovation with fiscal prudence.
By linking tangible assets (GPUs) to institutional capital, Musk may have unlocked a new pathway for AI startups to grow sustainably—one where risk is shared, capital is accessible, and hardware becomes more than a cost center; it becomes a financial instrument.
As the world watches xAI’s next chapter unfold, one thing is certain: this is more than a funding round—it’s a financial revolution for the AI age.
External Source: Reuters – Musk’s xAI nears $20 billion capital raise tied to Nvidia chips

Leave a Reply